News & Topics
ホーム > Research > News & Topics > A novel risk variant of late-onset Alzheimer's disease was found in genomic data from NCGG Biobank
In a new paper published in Journal of Human Genetics
published in Journal of Human Genetics on 5th Nov, researchers at the Medical Genome Center, Research Institute, NCGG have proposed a novel genetic factor associated with an increased risk of late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD). Dr. Yuya Asanomi, research fellow and lead author on the paper, and his colleagues found a novel LOAD-risk variant in SHARPIN by using whole-genome sequencing (WGS) data stored in NCGG Biobank
on 5th Nov, researchers at the Medical Genome Center, Research Institute, NCGG have proposed a novel genetic factor associated with an increased risk of late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD). Dr. Yuya Asanomi, research fellow and lead author on the paper, and his colleagues found a novel LOAD-risk variant in SHARPIN by using whole-genome sequencing (WGS) data stored in NCGG Biobank .
.
LOAD is the most common form of dementia and arises from complex interactions among multiple genetic and environmental factors. In 2019, the researchers identified a rare functional variant of SHARPIN (rs572750141, NP_112236.3:p.Gly186Arg) as a novel genetic risk factor for LOAD (odds ratio = 6.1) [Asanomi et al. 2019 ]. After that, two other SHARPIN common variants in Caucasian which are hardly detectable in Japanese were reported as LOAD-risk factors by large-scale genomic cohort studies in Europe and the United States. The role of SHARPIN in the pathogenesis of LOAD is currently drawing attention.
]. After that, two other SHARPIN common variants in Caucasian which are hardly detectable in Japanese were reported as LOAD-risk factors by large-scale genomic cohort studies in Europe and the United States. The role of SHARPIN in the pathogenesis of LOAD is currently drawing attention.
NCGG Biobank stores more than 3,000 WGS data of Japanese including dementia patients. In this study, the researchers used WGS data from 180 LOAD patients and 184 individuals with mild cognitive impairment, which is the precursor stage of dementia, to search for further LOAD-risk variants of SHARPIN. Six candidate variants predicted as highly deleterious were found in the exonic region of SHARPIN. Then, the association analysis was conducted by using the genotype data of 5,043 LOAD cases and 11,984 normal cognitive individuals stored in NCGG Biobank. As shown in the table below, one missense variant, rs77359862 (NP_112236.3: p.Arg274Trp), was found as a statistically significant LOAD-risk factor (odds ratio = 1.43). Furthermore, the researchers performed functional analyses of the variant-type SHARPIN. In HEK293 cells, the variant-type SHARPIN showed aberrant cellular localization and attenuated the activation of NF-κB, a central mediator of inflammatory and immune responses.
Table. Summary of association study of rs77359862 with the risk of LOAD
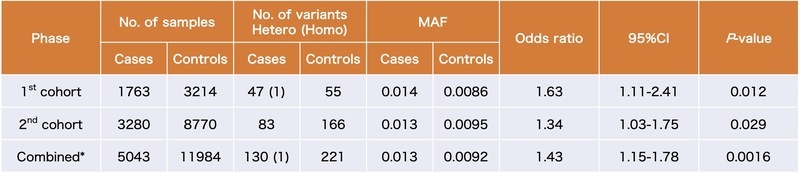
MAF; minor allele frequency, CI; confidence interval.
* P-value was calculated by using Mantel-Haenszel test.
The carrier of the variant, rs77359862, found in this study is 1-4% in Asian population while the carrier of rs572750141 is rare (<0.05%). Therefore, the present finding is more important in the clinical treatment of LOAD. Further research on the genetic relationship between SHARPIN and LOAD may elucidate the mechanism of LOAD pathogenesis and may provide new insights for the development of effective LOAD medication.
Title: A functional variant of SHARPIN confers increased risk of late-onset Alzheimer’s disease
Authors: Yuya Asanomi, Daichi Shigemizu, Shintaro Akiyama, Akinori Miyashita, Risa Mitsumori, Norikazu Hara, Takeshi Ikeuchi, Shumpei Niida, Kouichi Ozaki
Journal: Journal of Human Genetics
DOI: 10.1038/s10038-021-00987-x