Lab Drug Screening, Group 1 (2011/4 ~)
Researcher:
Tatsuya Yoshimi, PhD.
Research assistant: Mayumi Yamagishi, BSc.
Introduction
My family is originated from local Gamagori coast located 30km east
of the Center. I had
graduated Nagoya Univ. and taken a doctorate of biological chemistry in
Osaka
Univ. After working 12 years of research associate in Tokyo Univ. of
Pharamacy, I went to study at the Institute of Biotechnology, Univ.
Cambridge UK, for 2 or more years. After I did study for a while
surounding sheep or cow in the UK, I have got an telephone
call from Japan. It was an interview by Dr. Takikawa. So I'm here to
develop the robot screening system.
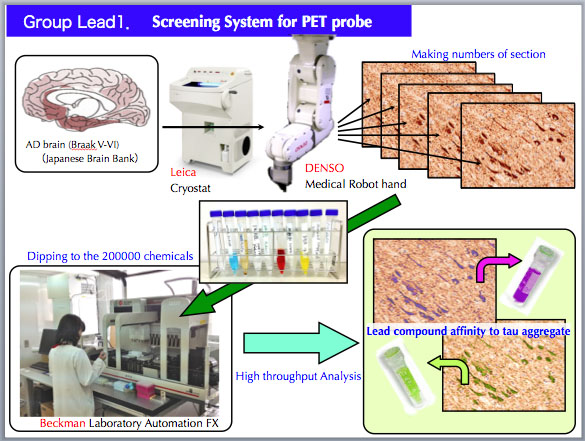
The system needs
several mechanical parts to screen the chemicals that have affinity to
the
aggregates in the human brain. Also needs chemical library, human AD
brain samples, and the administration systems. We have been building up
the total
high throughput system for screenig chemicals affinity with tau
aggregates.
Ms. Yamagishi has joined to assist the work from 2013.4. She has
graduated department of agriculture and 4 years' experience of working
at pharmaceutical company.
The photographs hanging right below are my hobbies, i.e. camera,
car, castle.
High throughput screening by robotic system.


Turning leaves in Japan

Cows in the UK

My old MR-2. (b. 1984)

Oxburgh hall in Cambridgeshire, UK

Iga-Ueno castle in Nara, Japan
Link
Contact
Tatsuya Yoshimi, PhD
Lab Drug Screening, Dep Drug discovery,
Center for Development of Advanced Medicine for Dementia (CAMD)
National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology
7-430, Morioka-cho, Obu-City,
Aichi 474-8511, Japan
e-mail: 
Access (-->Map)
Publications
| Lu
M, Williamson NR, Boschetti C, Ellis T, Yoshimi T, Tunnacliffe A.:
Expression-level dependent perturbation of cell proteostasis and
nuclear morphology by aggregation-prone polyglutamine proteins. J Biol
Chem, in press. |
| Wright O, Zhang L, Liu Y,ºYoshimi T, Zheng Y, Tunnacliffe A. Critique of the use of fluorescence-based reporters in Escherichia coli as a screening tool for the identification of peptide inhibitors of Aβ42 aggregation. J Pept Sci. 19:74-83, 2013. |
|---|
| Wright O*, ºYoshimi T*, Tunnacliffe A (*Equally contributed). Recombinant production of cathelicidin-derived antimicrobial peptides in Escherichia coli using an inducible autocleaving enzyme tag. N Biotechnol, 29:352-358, 2012. |
| Goto Y, Kajiwara M, Yanagisawa Y, Hirose H, ºYoshimi
T, Umemura M, Nakano H, Takahashi S, Shida Y, Iguchi T, Takahashi Y,
Miura T. Detection of vertebrate-type steroid hormones and their
converting activities in the neogastropod Thais clavigera (Küster,
1858). J. Mollus. Stud. 78(2): 197-204 first published online
February 20, 2012. |
| ºYoshimi T, Hashimoto F, Takahashi S, Takahashi Y: Suppression of embryonic lung branching morphogenesis by antisense oligonucleotides against HOM/C homeobox factors. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 46(8):664-72, 2010. |
| ºYoshimi T, Odagiri K, Hiroshige Y, Yokobori S, Takahashi Y, Sugaya Y, Miura T. Induction profile of HSP70-cognate genes by environmental pollutants in Chironomidae. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 28(2):294-301, 2009. |
| Manabe T, Takahashi Y, ºYoshimi T, Miura T, Sugaya Y. Development of an acute toxicity test for first-instar larvae of a midge (Chironomus yoshimatsui) using a Teflen-sheet. Jpn. J. Environ. Toxicol. 10, 51-57. 2007. |
| ºYoshimi T, Nakamura N, Shimada S,
Iguchi K, Hashimoto F, Mochitate K, Takahashi Y, Miura T.
Homeobox B3, FoxA1, and FoxA2 interactions in epithelial lung cell
differentiation of the multipotent M3E3/C3 cell line. Eur. J.
Cell Biol. 2005, 84: 555-566. |
| |
| [Presentation in abroad] |
| Mikawa R, Okuno A, ºYoshimi
T, Okada K, Takayanagi A, Takikawa
O. Implication of Brain Microvessel Endothelial Cell-derived
Beta-Amyloid Peptide in Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Associated with
Alzheimer's Disease. Alzheimer's Association International Conference
(AAIC) 2013, July 14, Boston, USA. |
| Okuno A, ºYoshimi T,
Okada K, Mikawa R, Takayanagi A, Takikawa
O. Pathogenic role of IDO in Alzheimer's disease : Astrocytes but not
neurons are responsible for the increase of amyloid β peptide induced
by neurotoxin quinolinic acid. International Society for Tryptophan
Research (ISTRY 2012), November 7, 2012,
Sydney, Australia. |
| Okuno A, Zhang G, ºYoshimi T, Mikawa R, Takikawa O. Aβ Production from Reactive Astrocytes Induced by Endogenous Neurotoxin Quinolinic Acid: A New Aspect of Alzheimer's Disease. Alzheimer's disease Association International Conference (AAIC) 2012, July 18, 2012, Vancouver, Canada. |



